Electret (formed of elektr- from "electricity" and -et from "magnet") is a dielectric material that has a quasi-permanent electric charge or dipole polarization. An electret generates internal and external electric fields, and is the electrostatic equivalent of a permanent magnet.
There are two types of electrets. Real-charge electrets which contain excess charge of one or both polarities, either on the dielectric’s surfaces (surface charge) or within the dielectric’s volume (space charge).
Oriented-dipole electrets contain oriented dipoles. Ferroelectric materials are one variant of these.
Some dielectric materials are capable of acting both ways, as shown in figure 1.
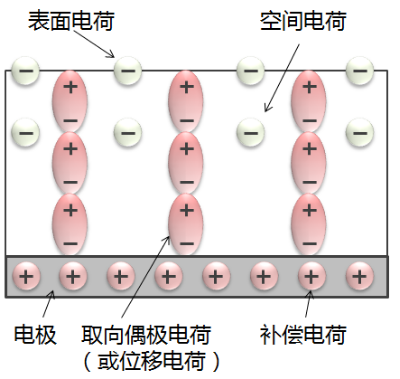
Figure 1. Charge distribution in Electret
One of the most successful application of electret is the electret microphone, which was developed by G. M. Sessler and J. West in Bell Laboratories, USA, in 1962. Besides, electret material is also suitable for air filtration.